(책)유연한 프로그래밍을 위한 설계원칙 조금 살펴보기
이번 글에서는 2장 영역 특화 언어(DSL) 초반부만 Python, javascript와 비교해보려고 한다. Jupyter notebook에서 커널을 각각 Python, Deno로 설정해 racket 코드를 그대로 구현해보려고 한다.
DSL
조합자
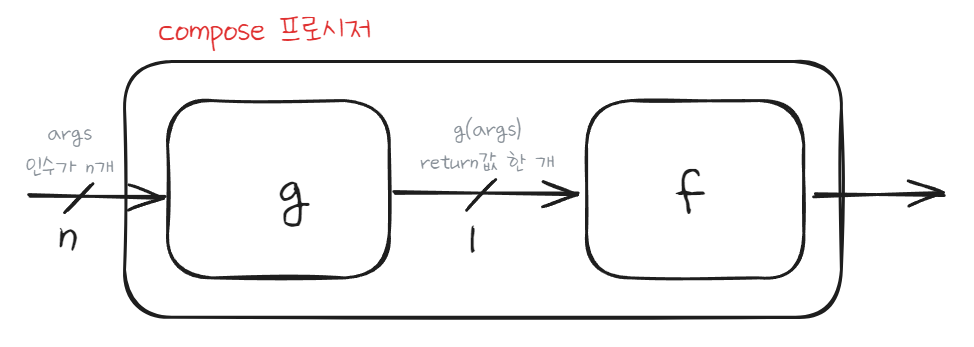
함수 조합자 compose는 고등학교 수학에서 배운 함수의 합성과 유사하다. 조합자는 두 개 이상의 함수를 인자로 받아 합성한 함수를 리턴한다. 다음 코드를 참고하자.
1
2
3
4
5
(define (compose f g)
(lambda args
(f (apply g args) )
)
)
위 코드의 예제는 아래와 같다.
1
2
3
4
((compose (lambda (x) (list 'foo x)) ;문자열 ['foo', x] 리스트 생성
(lambda (x) (list 'bar x)) ;문자열 ['bar', x] 리스트 생성
)'z); 문자 'z' 입력
'(foo (bar z)) ; 리턴값
조합자 내부 프리시저 이름 붙이기
이번에는 compose 프리시저 안에 함수 합성 결과물에 이름을 붙이고 싶다고 한다. 쉽게 말해서 lambda 함수를 사용하지 않고 함수 안에 함수를 정의하려고 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
(define (compose f g)
(define (the-composition . args)
(f (apply g args))
)
the-composition
)
조합자 응용 : 재귀함수
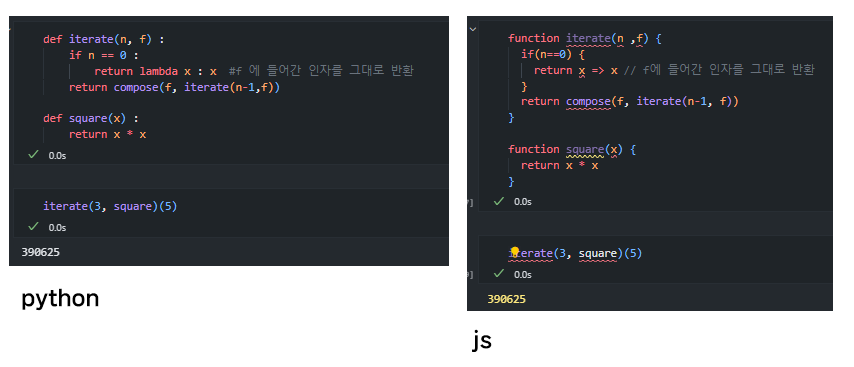
compose 조합자만으로도 $f^n(n) = f(f^{n-1}(x))$ 재귀함수를 구현할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
(define ((iterate n) f)
(if (= n 0)
identity ; racket의 return 키워드
(compose f ((iterate (- n 1)) f))
)
)
(define sqaure (lambda x (* x x)))
(((iterate 3) square) 5) ;390625
identity는 racket docs에 있는데return키워드랑 동일하다.racket문법 상(define (identity x) x)으로 보면 된다.
- 책에서는 위 코드처럼 적혀 있는데 아래처럼
(iterate n) f대신(iterate n f)처럼 적어도 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
(define (iterate n f)
(if (= n 0)
identity ; racket의 return 키워드
(compose f (iterate (- n 1) f))
)
)
((iterate 3 square) 5) ;390625
위 함수의 매커니즘은 아래와 같다.
\[(f \circ f \circ f)(5) = f(f(f(5))) = (((5^2)^2)^2) = 5^8 = 390625\]병렬 조합자
이번에는 두 가지 이상의 함수를 한 번에 합성하는 병렬 조합자를 살펴보자. 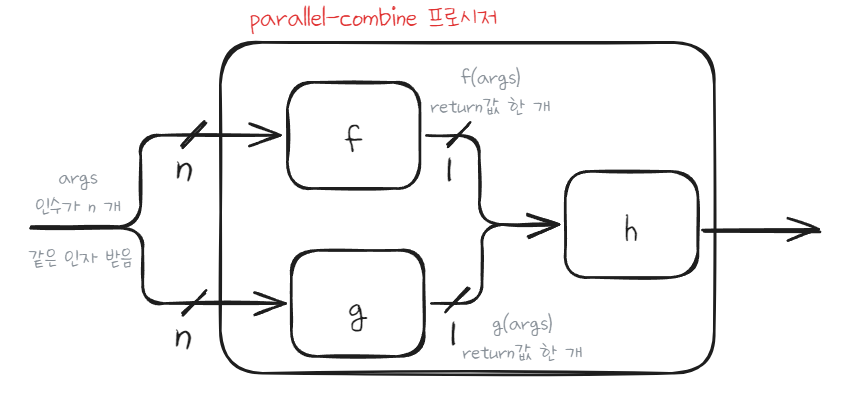
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
(define (parallel-combine h f g)
(define (the-combination . args)
h (apply f args) (apply args)
)
the-combination
)
((parallel-combine list
(lambda (x y z) (list 'foo x y z))
(labmda (u v w) (list 'bar u v w)))
'a 'b 'c)
이 병렬 조합자는 복잡한 과정을 조직화할 때 사용하면 좋다고 한다. 책에서 말하기를 여러 장의 채소 사진 이미지들을 입력하면 채소의 색상을 추정하는 프로시저 함수 f, 채소의 형태(잎, 뿌리, 줄기 등)를 서술하는 프로시저 함수 g를 조합해서 판정하는 프로시저 함수 h를 만들 때 위 방식으로 사용하면 깔끔하게 만들 수 있다고 한다.
항수
위에서 좀 더 발전시켜보면 arguments를 받으면 이들을 n, m개로 분할하여 각각의 프로시저에 대입하는 spread-combine을 만들 수 있다. 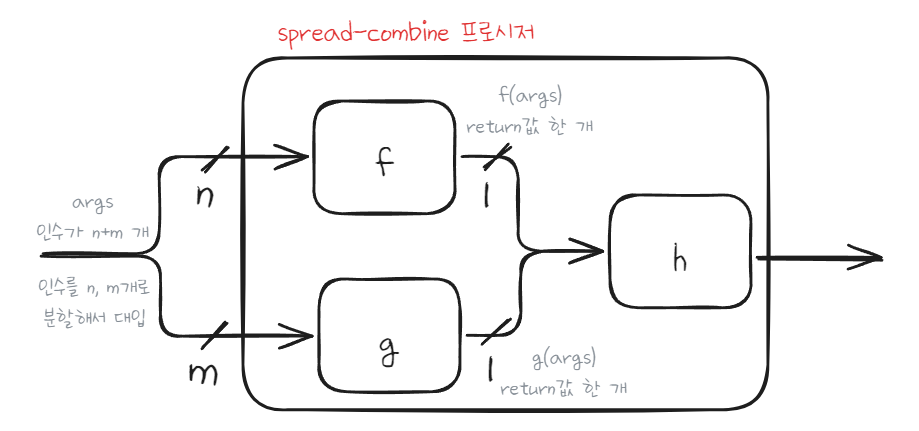
항수 프리시저 2개
책에서는 이 프리시저를 2개를 구현하기 전에 먼저 spread-combine을 구현한다. 아마 MIT/GNU Scheme 에 익숙하지 않은 사람들이 다음 코드를 이해하기 어려울 거라고 판단해서 그런 거 같은데, 한 번 구경이나 해보자.
참고로 여기서부터 racket에서 실행이 안 된다.
hash-table-set!같은 프로시저가Scheme에서만 사용되다보니 실행이 되지 않는다.
restrict-arity
프리시저 2개를 소개할 건데, 내용이 지나치게 길어졌다. 참고만 하고 넘어가자.
1
2
3
(define (restrict-arity proc nargs)
(hash-table-set! arity-table proc nargs)
proc)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
(define (get-arity proc)
(or (hash-table-ref/default arity-table proc #f)
(let ((a (procedure-arity proc))) ; 항수가 table에 없을 경우
(assert (eqv? (procedure-arity-min a)
(procedure-arity-max a))
)
(procedure-arity-min a)
)
)
)
(define arity-table (make-key-weak-eqv-hash-table)) ;MIT/GNU Scheme
- hash-table-set!
hash-table key datum- Associates datum with key in hash-table and returns an unspecified result.
- key값에 datum 대응하기
- or
- 위 코드에서 첫 번째 줄인
(hash-table-ref/default arity-table proc #f)코드에서arity-table에proc키가 없어서#f를 반환해서 그 다음 코드인let구문을 실행하는 과정이다. - 만약
arity-table에proc함수가 키로 등록되어 있다면 이미 등록된 항수procedure-arity값을 반환한다.
- 위 코드에서 첫 번째 줄인
- hash-table-ref/default
hash-table key default(hash-table-ref hash-table key (lambda () default))- hash-table-ref
hash-table key [get-default]- Returns the datum associated with key in hash-table. If there is no association for key, and get-default is provided, it is called with no arguments and the value it yields is returned; if get-default is not provided, an error is signaled.
- procedure-arity
- 프로시저
proc가 몇 개의 인수를 받을 수 있는지 항수를 반환한다.
- 프로시저
- assert
- 실행하고자 하는 프로시저가
#f를 반환하는지 안 하는지 확인하는 키워드다. - 만약 프로시저가
#f를 반환하면 에러를 호출한다.Assertion #<procedure: ()?> failed on ...
- 실행하고자 하는 프로시저가
- eqv?
- 메커니즘이
==이랑 조금은 다른데, 일단 여기서는 정수,실수형, 문자열이 같으면true #t반환 , 두 인수가 다르면false #f를 반환한다는 점만 알고 있으면 되겠다.
- 메커니즘이
- procedure-arity-min, procedure-arity-max
- Return the lower and upper bounds of arity, respectively.
- make-key-weak-eqv-hash-table
- 프로시저 중 하나
- Returns a newly allocated hash table that accepts arbitrary objects as keys, and compares those keys with
eqv?. The keys are held weakly, except that booleans, characters, numbers, and interned symbols are held strongly. The data are held strongly. Note that if a datum holds a key strongly, the table will effectively hold that key strongly. - 대충
key-datum해쉬 테이블 타입 인스턴스를 하나 만든다는 의미인 거 같다.- key에는
bool,char/string,int/float,interned symbol(:,$.등의 특수 문자를 넣은 문자열 느낌)가 올 수 있다.
- key에는
MIT/GNU Scheme에 대한 사전지식이 없어 위 코드들을 온전히 이해하지 못했는데 python과 javascript로 흉내를 내보면 다음과 같은 코드로 치환할 수 있을 거 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
import inspect # 인수 개수 확인하기 위한 모듈
# arity_table 선언
ip = inspect.Parameter
arity_table = dict()
# get_arity 선언
def get_arity(proc) :
if proc in arity_table.keys() :
return arity_table[proc]
a = inspect.signature(proc).parameters.values()
#편의상 min_args, max_args 따로 선언
min_args = 0
max_args = 0
for p in params :
max_args += 1
# *args, * 이후 인수, **kwargs 이면 min_args 추가X
if p.kind not in [ip.VAR_POSITIONAL, ip.KEYWORD_ONLY, ip.VAR_KEYWORD] :
min_args += 1
assert min_args == max_args, "Abort! min_args != max_args error."
return min_args
# restrict
def restrict_arity(proc, nargs : int) :
arity_table[proc] = nargs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
const arity_table = new Map(); // HashMap
function get_arity(proc) {
if(arity_table.has(proc))
return arity_table[proc]
const minArity = proc.length;
const paramString = proc.toString().match(/\(([^)]*)\)/)[1]; // 괄호 안 인수 개수를 세는 정규표현식
const hasRestParams = paramString.includes('...'); // 인수에 spread문법 ... 포함되는지 체크
const maxArity = hasRestParams ? Infinity : minArity;
if (minArity !== maxArity) {
throw new Error("Min and Max arity do not match");
}
return minArity;
}
function restrict_arity(proc, nargs) {
arity_table.set(proc, nargs)
//arity_table[proc] = nargs로 값을 넣으면 arity_able.has(proc)에서 항상 false 값을 뱉는다.
}
python, JS로 고쳐도 코드가 상당히 복잡하다.
get-arity코드와restrict-arity코드가 의미하는 바를 내 방식대로 요약해보자.
get-arity: 전역변수arity-table에proc프로시저가 있으면 항수를 반환하고 없으면proc에 들어가는 최대 최소 항수가 같다면 최소 항수를 반환한다.restrict-arity: 전역변수arity-table에proc프로시저에 항수 값을 넣는다. (인수를nargs개만큼만 들어가도록 제한)
실전이면 get-arity나 restrict-arity를 따로 구현해놓거나 다른 방법으로 spread-combine 프로시저를 구현해야 할 거 같다.
ver 1. 함수 f의 항수만 정의
get-arity사용restrict-arity사용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
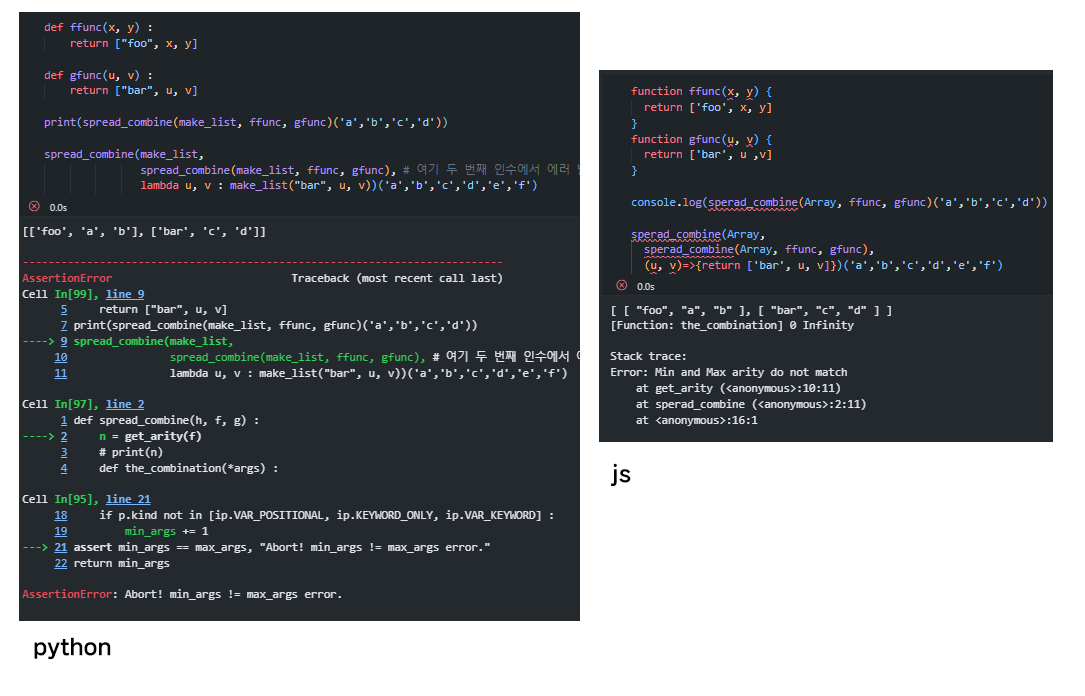
(define (spread-combine h f g)
;let은 지역변수 선언 키워드
;let n = get-artiy(f) 같은 코드
(let ((n (get-arity f)))
(define (the-combination . args)
(h (apply f (list-head args n))
(apply g (list-tail args n)))
)
the-combination
)
)
;예제
((spread-combine list
(lambda (x y) (list 'foo x y))
(lambda (u v) (list 'bar u v)))
'a 'b 'c 'd 'e)
- 이 버전의
spread-combine은 좋은 코드가 아니다.- 가장 큰 문제점은
the-combination프로시저가 임의의 개수의 연수를 받으므로 항수의 구체적인 숫자가 정의 되지 않아 항수를 요구하는 다른 조합자에게the-combination을 전달할 수 없다. - 예를 들어,
spread-combine의 결과를 다른spread-combine의 둘째 인수f로서 전달할 수 없다.spared-combine(h, spread-combine(), g)- 받는 인수크기가 안 정해져있기 때문이다.
- 가장 큰 문제점은
보시다시피, 재귀함수처럼 spread_combine 안에 spread_combine을 넣으니 Assertion 에러가 발생한다. 이는 the-combination이 arity_table에 등록이 안 되어 있어 get_arity를 호출할 때, the-combination가 assertionError을 발생시킨다.
따라서 the-combination에 적절한 항수를 부여해야 한다는 건 arity_table에 the-combination을 등록시켜 get_arity 함수의 조건문을 타서 탈출하게 만드는 것이다.
ver 2
get-arity사용restrict-arity사용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
(define (spread-combine h f g)
(let ((n (get-arity f)) (m (get-arity g)))
(let ((t (+ n m)))
(define (the-combination . args)
(h (apply f (list-head args n))
(apply g (list-tail args n)))
)
(restrict-artiy the-combination t)
)
)
)
이제 spread-combine 내부 the-combination 항수를 제한함으로써, spread_combine 재귀 표현은 사용할 수 있다.
ver 3
get-arity사용restrict arity사용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
(define (spread-combine h f g)
(let ((n (get-arity f)) (m (get-arity g)))
(let ((t (+ n m)))
(define (the-combination . args)
(assert (= (length args) t))
(h (apply f (list-head args n))
(apply g (list-tail args n))
)
)
(restrict-arity the-combination t)
)
)
)
아까 코드에서 혹시 모를 버그를 미리 방지하기 위해 assert 구문을 추가했다. python, js 코드에도 the_combination 내부에 t != len(args) 일 때 에러를 일으키는 구문을 추가해주면 된다.
%%항수에 관한 내용을 도식으로 표현할려고 했으나 시간 부족으로 생략ㅠ%%
아무튼 이와 같은 방식으로 racket이라는 생소한 코드를 이해하려고 하면 책의 저자가 말하고자 하는 프로그래밍 스타일에 대해서 이해하는데 도움은 될 것이다. 영어 공부할 때 일일이 번역하는 것처럼 많이 비효율적일 수는 있겠지만, 처음보면서 꽤 유익한 프로그래밍 스타일이 많아 천천히라도 공부해보는 것도 좋을 것 같다. ■
- 2024-08-23
- GPT에게 물어보니 어떤 원리인지 잘 설명해준다. 아리까리한 코드를 보일 때마다 검색하면 아주 친절하게 잘 알려주니까 GPT를 잘 활용해보자.
Reference
- (번역본 책)유연한 프로그래밍을 위한 설계 원칙
- Racket에 MIT/GNU Scheme 실행하기
- 시도해봤지만 “항수” 챕터 코드를 실행하지 못했다..
- Julia (Lisp) 언어에서의 interned string
- interned string이 뭔가 해서 검색했는데 lisp에 쓰이는 특수 문자열 같은 거다.